You often hear about Google's 200+ ever changing ranking factors and the challenges these present to SEOs, business owners and marketing professionals. Personally I think talking about all 200+ factors is overkill. I believe for a lot of businesses real results can be found by managing just 22. With commentary from industry leaders from at HubSpot, Kissmetrics, Go Compare and eBuyer to name a few , unless you plan to be an SEO guru, this is the only Google ranking factors list you'll ever need to read!

Many people talk about Google’s 200+ ranking factors and when they do this I unfortunately believe a lot of people do it to make their job sound more complex than it really is or to create a mystique around the SEO industry to protect themselves. I really hate these things about the SEO industry so in an effort to make it more transparent I have narrowed the ranking factors down to 22 you really need to know and split these by link based factors and on-site factors.
To help you even more I reached out to a handful of industry experts who have provided us their exclusive comments, look out for these throughout the piece!
Page authority is a metric from SEO software company Moz which scores the strength of a page on a scale from 1 to 100. It is important because it predicts how well a page will perform in Google, allowing you to directly compare your page with a competitor’s page. You can check your page authority on Open Site Explorer from Moz.
To increase your page authority you need to earn links, not only to your homepage but also to deeper pages within your site. Secondly, you'll need to look at the architecture of your site to ensure pages you want to rank for are getting a flow of authority from your homepage. As the diagram below shows the further from the homepage a page gets the less authority is passed through...
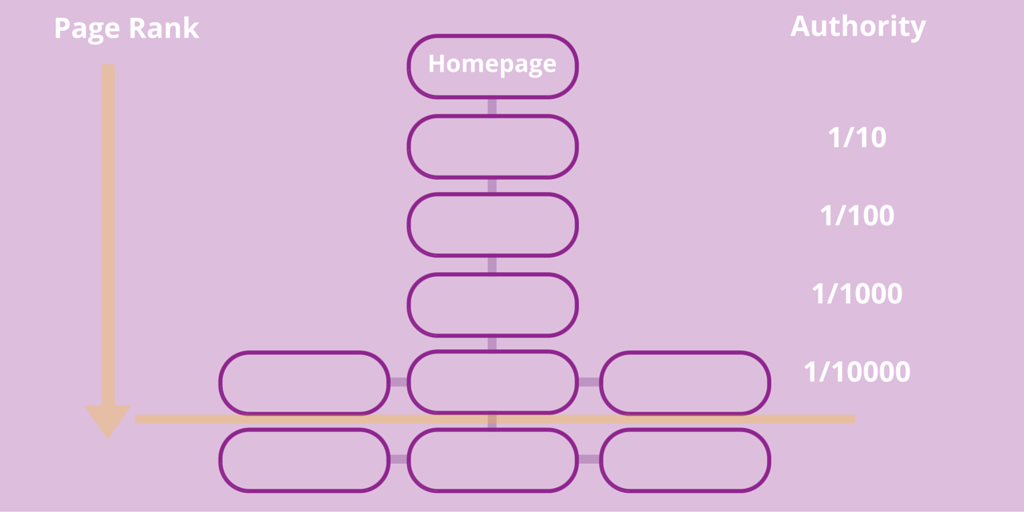
2. Domain authority
Domain authority is the strength of your whole website (unlike Page authority above which is a metric for an individual web page) in the eyes of search engines. Sites with higher domain authority are able to rank easier for competitive queries. That's why you see sites such as Wikipedia, Amazon and eBay for a lot of searches you make, even if they are not the most relevant.
Domain authority is a metric provided by Moz.
Your domain authority is influenced by the volume, quality and relevance of links pointing into your website which we will now look at.
3. Number of links
A link, in SEO terms, is one website links to another and, no matter what you read elsewhere, links are still essential to rankings. The pure number of links pointing to your website is a big part of where you rank and the amount of organic traffic you attract, with one huge caveat. Today, quality links are very beneficial whereas poor links count against you (more on this point later). When trying to earn links you need to ensure that link volume is taken into account but never at the expense of quality.
4. Number of unique links
Whilst talking about link quantity, it's important to differentiate the number of links from number of unique links. When referring to unique links here we are talking about links from different websites (or domains). This is because every time you get a link from a website you already have a link from the 'power' awarded to each subsequent link is reduced. To receive the maximum benefits from quality links, you will need to earn a varied link profile featuring unique websites.
5. Quality of links
I would argue that of all the link factors I have mentioned so far - this is the most important. Earning links from reputable sources is key to ranking highly in competitive industries.
Quality of links certainly wins over pure volume, and that isn't going to change. If you can't invest much time outreaching to lots of different people with good authority - spend your time pitching to one or two with excellent authority, but remember that these sites will get dozens of requests for links everyday so make your proposition unique and beneficial to both parties. What's more, taking this approach will safeguard your business by ensuring you don't get penalised.
In this Whiteboard Friday Rand discusses why some links don't help you rank higher (hint, it's because of quality of these links):
6. Relevancy of links
The relevancy of the links you earn play a big part on how you rank. Assuming two links are equal in terms of quality and authority a link from a website which is related to your niche or target keyword will help more. This is because Google is getting smarter at understanding the context of a website, not just the words on the page, so it can now figure out if the website linking to you is from a related source or not, and they give extra weighting to links which are.
7. Anchor text
Anchor text (the clickable text in a hyperlink) still influences search results and has a heavy weighting. However it is also a spam signal to Google's if abused (more on this later). Our advice is to let the webmaster select your anchor text for you, however if you have full control over the anchor text use a natural keyword matching anchor text where appropriate. Here's an example of natural keyword matching anchor text:
"... so now you know about all the marketing options available to you. If you think inbound is the best option for you click here to learn more about inbound marketing."
And here is an example of an obvious keyword matching anchor text:
"... so now you know about all the marketing options available to you. If you think inbound is the best option for you read our resource; what is inbound marketing."
As previously mentioned, Anchor text has a dark side, make sure you don't fall foul to these negative link base ranking factors...
8. Over optimised anchor text
As discussed anchor text can be a positive but it can also be a negative. Over optimised anchor text (anchor text which mentions the keywords you are targeting) is very easy for Google to figure out if someone is using manipulative link practices. Here is an example of an over optimised anchor text profile, I would suggest this website is playing a dangerous game (which isn't unusual in the pay day loans sector):
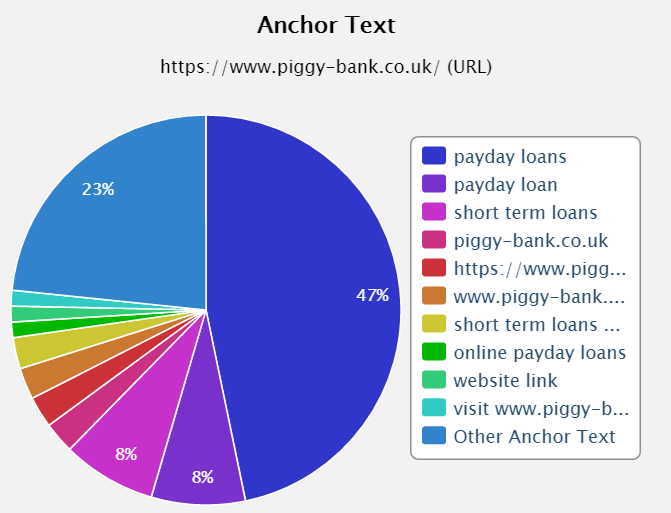
As you can see well over half of their anchor text matches their keywords, whereas a healthy back link profile would look like this:
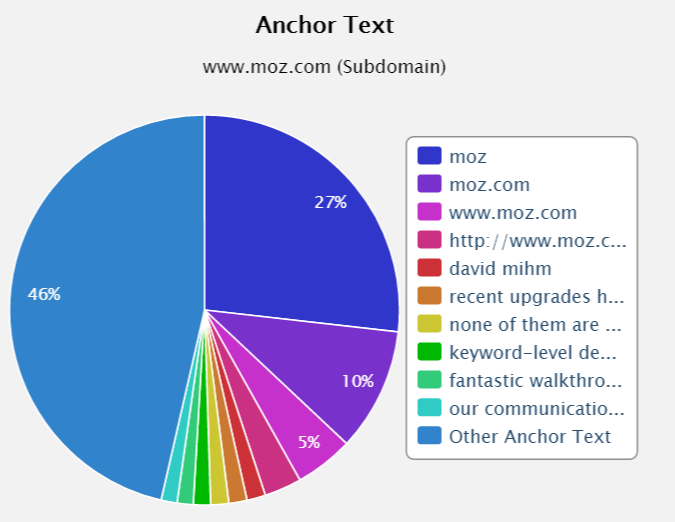
As you can see the profile is predominantly brand related and has very high diversity.
9. Number of unnatural links
We have spoke a lot about the benefits links can have but it's worth noting that links can do damage as well. If you try and 'game' Google by building links in an automated or spammy way (such as blog commenting, SEO directories or building link networks) you will be penalised. That's why we call the process link earning and not link building - you need to put value out to the web to attract links to you, rather than artificially building them.
Here is a video of Matt Cutts explaining why unnatural links are bad for users and how they can cause penalties:
So, if you come across an email like this, save yourself $150 and the hassle that would come with it...

10. Keyword in title tag
It's a basic one but very important!
The title tag is the large header on a website listing in a search engine, as illustrated below in purple:
Having your chosen keyword in the title tag is one of the strongest signals which Google uses to determine your page content and relevancy to a search query. We recommend a title tag structure which targets 2 keywords, your brand name and a USP (to encourage more people to click your listing). This would look like:
<Keyword 1> from <Brand> | <Keyword 2> with <USP>
or using keywords:
Running Shoes from RunStore | Running Trainers with Free Delivery
11. Query to page relevance
It may sound obvious but you're only going to rank for a keyword if the page is relevant to the query the user is searching.
Google does this for a reason - if the content on page doesn't exactly match what the searcher expects to see, the page isn't going to help the user. This creates a bad searching experience which Google wants to discourage. Don't forget that chasing a high rank with irrelevant content and keywords will not help you in the long run so it's best to avoid it all together.
Creating relevant, helpful content is key to a successful Inbound strategy. Read our Inbound eBook to see just how big the impact could be for you:
12. Uniqueness of page content
Google is less likely to rank a page well if the content has been produced and published elsewhere. This is to stop people benefiting from other peoples work.
Ramsay Taplin from Blog Tyrant gave us his advice when it comes to uniqueness of page content:
"When you take a look at the front page of Google you'll notice lots of different things. You'll see images, videos, tweets, news stories, old articles from the 90's and sometimes even live results or details (think about the weather...). When someone uses Google they are trying to solve a problem that they have. Google wants to show its customers a variety of different solutions in the hope that one of them helps them in a genuine way.

As a content producer you need to be mindful of this thinking. Jump on Google and do a few searches for your target key phrases and see what is appearing on the front page, and then think to yourself: "How can I add something different or better to this mix?".
Sometimes you can create a new tool, graphic or create a piece of massive long-form content that improves on everything out there. By being new, unique and having a slightly different voice you will find that Google is much more likely to index you prominently - and sometimes that is simply because more people are linking to you as a solid resource."
13. Keywords on page
Not only are relevant keywords important in your title tags, they need to be part of your page content too. Sound like common sense? That's because it is. By having keywords about genuine services you offer or products you sell, Google can understand why that particular page exists and if it is a suitable page to be returned in search results. Google is getting much smarter at understanding the context of a page so spread your bets by making sure you include keyword variations.
For example:
Keyword - Inbound marketing agency
Variants - Digital marketing, inbound, marketing agency, SEO, email
Once again - this isn't SEO wizardry and should happen naturally if your keyword targeting and page content match. Don't force keywords into your page where they don't fit or it will ruin the visitor experience.
14. Thin content / page length
Thin content is a phrase used to describe low quality and low value pages which offer very little to the user. Google introduced the Panda update to reduce the rankings of these pages. Below is a video from Google's Matt Cutts on the subject:
There is also positive correlation between page length and rankings. This is illustrated below in a study by serpIQ:
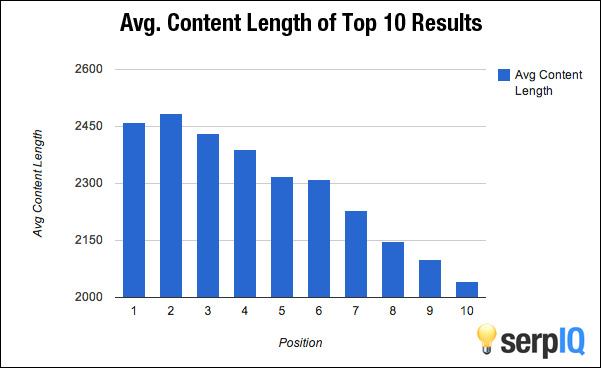
Now, don' take the wrong message from this and think you need to go away and make all your pages 2,500 words so you rank #1.
The above data can quite reasonably be attributed to the idea that the articles that tip over the 2,000 word mark are more likely to be in depth, useful and well researched topics that offer the user honest and actionable insight.
Use this correlation data as motivation to make your pages as detailed and helpful to users as possible, just don't waffle on for the sake of word count!
15. Mobile friendly
Mobile friendly is a term which is used to describe websites which provide users on mobile devices a great experience. Due to the rapid rise in the amount of people accessing the web from mobile devices Google decided that it would be a good idea to make the mobile friendly test a ranking signal.
Andrew Isidoro, SEO Manager from Go Compare, provided us with his thoughts on the importance of being mobile friendly for ranking benefits:
"Every year users are spending more and more time on their mobile devices, but many sites are still not able to support a world of multiple screen sizes and slower connections. Marketers need to take a good hard look at site design, site structure, page speed, and more to make sure mobile visitors are being catered for properly.

Google's Mobile-Friendliness tool will give you a 'yes' or 'no' answer on a per-URL basis and can guide you on how to improve your site. Google's Webmaster tools can highlight issues with individual pages to be fixed but it's always worth testing at a local device lab to check across multiple devices."
16. Load speed
Load speed is a measure of how fast your web pages load. It has been deemed a ranking factor by Google as load speed directly effects the experience a user has. Today, no one expects to wait for a website to load. In fact, 25% of people give up on a website if it loads slower than 4 seconds!
Here is an explanation from Google's Matt Cutts:
Google have a page speed test available for free which also gives information about how to improve the speed as well. Alternatively the Website Grader will measure your sites speed as well as other factors contributing to the overall strength of the site.
17. User experience and metrics
Many of the factors in this list focus on the emotions and attitudes people have towards a website, this is called user experience and is key to modern SEO. You can gauge the success of your user experience, not just through your rankings, traffic and sales but through user metrics. These can be found in Google Analytics and include metrics such as time on site (how long the average person stays on the website) and bounce rate (how many people leave without taking a further action).
Co-founder of Crazy Egg and Kissmetrics, Neil Patel, gave Digital 22 his opinion on user experience and sums up the sentiment:
“The future of SEO is going to be user experience. Marketers are trying to game the system when in reality Google is just trying to give users what they want. If you can focus on improving your user experience, in the long run, you will win.”

Matthew Barby Global Head of Growth & SEO at HubSpot also gave us his thought on user experience:
“User experience is one of the most neglected elements of SEO but is becoming more and more powerful for ranking well in the search engines. Ensuring that the expectation of a user is met would be one of my top priorities when creating any content that I'm looking to drive organic search traffic to.

Having large proportions of your organic search traffic bounce has been shown in a number of studies to have a negative impact in the SERPs. On the flip side, seeing increases in search volume against your brand name along with keywords you're ranking for is being seen positively by Google.”
18. Keyword in URL
Another basic one but with high influence is having the keyword in your URL. Doing this will help you rank better for the keyword you are targeting. This doesn't mean you need an exact match domain, i.e. www.yourkeyword.com, you can include the keyword in the full URL string, i.e. www.yourbrand.com/your-keyword.
Not only does this appease Google, but a matching URL keyword or variation will be shown in bold in search results, drawing the searchers attention and building the impression that your page is useful, relevant and worth visiting. As you can see in the example below when I searched for "heat mapping software"...

19. Quality of content
To rank well today you really do need to offer something of quality, particularly in highly competitive industries. Ask yourself, does my site offer something that is useful to visitors and is it different to my competitors? If the answer is no then think about how you can add the maximum amount of value to the person searching for the keyword you are targeting.
A good first step for some companies is to create an FAQ which could help the user understand what the product / service is, how it can help them, how it works and how much it costs - all the questions you would want to know when purchasing something.
We do this on our own website...

For each piece of content you should aim to;
- Target the key problems for your target personas
- Answer the questions these personas ask your sales reps
- Offer authoritative insight about and beyond your competitors
- Use your industry knowledge and prove to your visitors you are an expert
20. Structured mark-up
Structured mark-up is a technique used to provide information to search engines on how you would like your site represented in results. If done correctly, key information will be presented in the results page to help the searcher and entice them to choose your page.
Schema.org is the current recommended mark-up structure and is supported by Google, Bing, Yadex and Yahoo!. Common uses of Schema markup are:
You can find out more information and use cases here as well as listen to Matt Cutts from Google talking about the benefits of implementing Schema below:
Again, there are a couple of key negatives to look out for with on-site factors too...
21. Keyword stuffing
Before search engines became more robust and advanced, people were able to 'game' them by stuffing keywords into their website to make it seem like it was very relevant. Whether that was stuffing the page copy itself, the footer and trying to hide it behind other objects.
Not only do these tricks not work anymore and haven't for some time - they are very likely to get you penalised. As we have discussed previously, take time to write unique content and design your pages for maximum visitor experience first and foremost, there are no shortcuts!
22. Outbound links to spam
A sign that your website is of poor quality is when it is seen to feature links to 'spammy' websites. When you put a link on your domain, Google sees this as a considered decision to give said site a vote of confidence. If the site is 'bad' in Google's eyes, this bleeds through to your domain by association.
This doesn't mean you should stop linking out from your site, the web is built on links. As you have seen I have linked out to dozens of sites in this post. Just don't associate yourself with the wrong sites and you'll be fine!
Andrew Halliday, Head of SEO and Web Analytics for Ebuyer.com, wanted to let you know about the importance of having a great meta description:
“Yes, we all know Google doesn’t actually use meta descriptions in terms of rankings anymore, yet they can still be a ranking factor.
There is a lot of talk about CTR, onsite signals, plus a lot more being important ranking factors, but no one ever seems to mention the actual meta description.
This is really the first thing a potential visitor sees about your brand. If it’s boring and badly written; who is going to click through? Whereas if you have a great description that stands out and accurately reflects the content of the page, the user is going to be happy, which then affects the rankings, as your CTR increases, you get lower bounce rate, and more interactions etc. These are all positive signals to Google.

An issue facing site owners is that different meta descriptions can’t easily be tested in organic search. However, this is where your friends over in the PPC team can really help you out. For any page on which you want to improve the meta description use your SEO tools to discover all the keywords the page ranks for. Then create a new campaign in Adwords using all those keywords.
Create several different ads and measure the impact on CTR. All other factors including Revenue, Cost of Sale, ROI can be ignored. In this instance you are only looking for CTR. The ad with the best CTR becomes your new meta description.
This method does require you having a small budget for PPC which may not convert but the long term benefits to organic traffic should see those costs recouped.”
Get a HUGE SEO shortcut
Do you want to take all this knowledge with you?
We've compiled ALL our ranking factor knowledge into the following FREE download.
Grab the printer-friendly PDF or choose the editable excel worksheet - whatever works best for you:
Real Growth. Real Impact.
Time to rethink your whole SEO and content marketing strategy
Why it's vital and how to start building customer-led sales and marketing
How is AI disturbing Google search results and what can you do about it
How to avoid over optimising your website with Hannah Wilson, SEO Specialist
Google Search API leaks: All you need to know [LIVE BLOG]
Choosing between a HubSpot Partner and an SEO-specific agency
What's happening with Google SGE and what should we do?
See why enterprises chooseAvidly
Let’s build your HubSpot success story
Compelling final call to action - with accompanying link to Contact page








![Google Search API leaks: All you need to know [LIVE BLOG]](https://www.avidlyagency.com/hs-fs/hubfs/cloud.jpg?width=400&height=225&name=cloud.jpg)


